In the last decade, they were posted 17 million dental implants in SpainAccording to the company’s international market KeystoneThe questionnaire this figure, which grows without a pause, reflects an important transformation on the path of understanding ORTH OF ORTHODThe Implantation questionnaires are no longer considered as an extreme solution, but as Normal replacement which guarantees functionality, duration and appearance.
However, there is Fundamental function This has not yet been reproduced at all. This drawback has just been eliminated by the team from the University of Tafts with a proposal that goes beyond the mechanics.
The intermediate layer allows you to restore sensations, connecting the implant to the nervous system
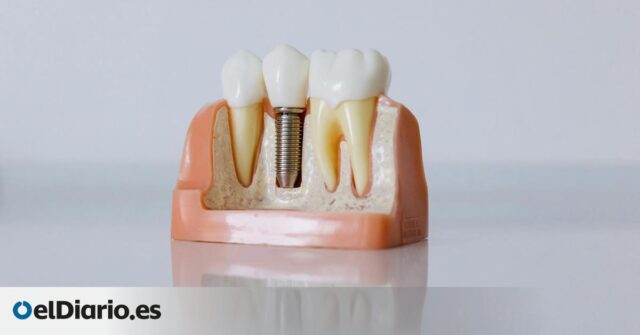
The main difference is not in the material or in the form of the implant, but what This happens between the screw and the boneProfile Provisor new model tested on rodents, Avoid direct merging with the jaw To ensure the growth of an intermediate layer of soft tissues. This membrane that is absent in traditional implants is key, because it serves as a way for Nervous terminations rest with the central nervous systemThe profiles of this sensory recovery completely change the behavior of prostheses in the mouth.
Researchers illuminated the implant Biodegradable layer Made of elastic nanofibers. The lining is designed to adapt to the cavity through A progressive expansion systemSimilar to the work of compressed memory foam. Inside they joined Stem cells Along with growth protein, known as FGF-2This directs the regeneration of nervous tissue. The intention is that this combination launches Biological reunion Restore part of lost sensitivity.
This sensitivity, called Dental propiocumentwas absent in all implants made so far. The reason c elimination of the periodontal ligament, A soft layer with abundant nerve endings, which connects a natural tooth with a bone. When the play is replaced by a fixed titanium implant, this sensory connection disappears, which changes both the perception of chewing and some nuances of speech.
The first animal results open the door for future clinical applications
The authors of the study are described in detail in Scientific reports The test results took place six weeks after the operation at rodents. On the images received by the scanner, they noticed that The implant was not welded to the bone As in traditional models. Instead, it remains suspended in the usual space from 0.7 to 0.9 millimetersIt is supported by a new tissue in regeneration. This controlled separation opens the likelihood that the nerve fibers grow around the implant.
The team explained that the promotion of advancement is not only in the design of the implant, but also in A way to place itThe profiles instead of drilling bone, as is usually done, Less invasive method Which consists of an insert of the prosthesis into a slightly wider alvets. Thus, the expansion of the covered material allows you to fix the implant Soft compressionWithout damage to the nerve structures that surround the hole.
Jake Dzhinkun ChenThe chief researcher of the Taft Dental Medicine School explained that the purpose of this new system goes beyond the preparation of the aesthetic crown for the jaw. In his analysis, published by the university itself, he indicated that “natural teeth are connected to the bone through the soft nervous tissue, which Help detect pressure and texture And direct how we will chew and talk. ”
The following tests will allow you to find out if the system reports real sensations
Until now, ordinary implants served as a functional solution of loss of teeth, but, acting as inert parts, they cause Excessive use of force when chewingChanges in the mandibular joint and small changes in speech. The purpose of the new design andS restore the bond cycle between teeth, jaw and brainWhat was lost during distribution with a natural ligament.
The following stages of the study include measuring the brain activity of rodents to check whether the new nervous network created by the implant transmarizes with real pressure or temperature signals. If this connection is confirmed, the researchers will go to Tests in larger animals before the start of clinical tests in peopleSaint himself said the questionnaires that “this new technique can also be used in other bone implants, such as those used in fractures of the hip joint or replacement.”